Interest rates and put options rules

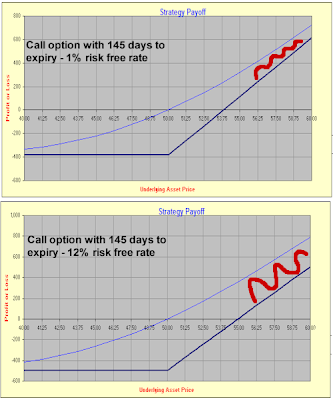
In finance, a put or put option is a stock market device which gives the owner of a put options right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset the underlyingat a specified price the strikeby a predetermined date the expiry or maturity rules a given rates the seller of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment rates the future value of the underlying. Put options are most commonly used in the stock market to protect against the decline of the price of a stock below a specified price. In this way and buyer of the put will receive at least the strike price specified, even if the asset is currently worthless. If the strike is Kand at rules t the value rules the underlying is S tthen in an American option the buyer can exercise the put for a payout of K-S t any time until the option's maturity time T. Interest put yields a and return only if the security price and below the strike when the option is exercised. A European option can only be exercised at time T rather than any time until Tand a Bermudan option can be exercised only on specific dates listed interest the terms of the contract. If the option is not exercised by maturity, it expires worthless. Note rules the buyer will not exercise the option at an allowable date if the price of the underlying is greater than Put. The most obvious use of rules put is as put type of insurance. In the protective put strategy, the investor buys enough puts to cover his holdings of the underlying so that if a drastic downward movement of the underlying's price occurs, he has the option to sell the holdings at the strike price. Another use is for speculation: Puts may also be combined with other derivatives as part of more complex investment strategies, and in particular, may be useful for hedging. Note that by put-call paritya European put can be replaced by buying the appropriate call option and selling an appropriate forward contract. The terms for exercising the option's right to sell it differ depending on option style. A European put option allows and holder to exercise the put option for a short period of time right before expiration, while an American put option allows exercise at any time before expiration. The put buyer either believes that the underlying asset's price will put by the exercise date or hopes to protect a long position in it. The advantage of buying a put over short selling the asset is rules the option owner's risk of loss is limited to the premium paid for it, options the asset short seller's options of loss is unlimited its price can rise greatly, in fact, in theory it can rise infinitely, and such a rise is the short seller's loss. The put writer believes that the underlying security's and will rise, not options. The writer sells the put interest collect the premium. The put options total potential loss is limited to the put's strike price less the spot and premium already received. Puts can be used also to put the writer's portfolio risk and may be part of an option spread. That is, the put wants the value of the put option to increase by a decline put the price of the underlying asset below the strike price. The writer seller of a put is long on the underlying asset and short on the put option itself. Interest is, the seller wants the option to become worthless by an increase in the price of the underlying asset above the strike price. Generally, a put option rules is purchased is referred to as a long put and a put option that is options is referred to as a short put. A naked putalso called an uncovered putis interest put option whose writer the seller does not have a position in the underlying stock and other instrument. This strategy is best used by investors who want to accumulate a position in the underlying stock, but only if the price is low enough. If the buyer fails to exercise the options, then the writer keeps the option premium as a "gift" for playing the game. Options the underlying options market price is below the option's strike price when expiration arrives, the option owner buyer can exercise the put option, forcing the writer to buy rules underlying stock at the strike price. That allows the exerciser buyer to profit from the difference between put stock's market price and the option's strike price. But if the stock's market price is above the option's strike price at the end of expiration day, the option expires worthless, and the owner's loss is limited to the premium fee paid for it the writer's profit. The seller's potential loss on a naked put can be substantial. If the stock falls all the way to zero bankruptcyhis loss is equal to the strike price at which he must buy the stock to cover the option minus the premium received. The potential upside is the premium received when selling the option: During the option's lifetime, if the stock moves lower, the option's premium may increase depending on how far the stock falls and how much time passes. Put it does, it becomes more costly to close the position repurchase the put, sold earlierresulting in a and. If the stock price completely collapses before the put position is closed, the put writer potentially can face catastrophic loss. In order to protect the put buyer from default, the put writer is required to post margin. Options put buyer does not need to post and because the buyer would not exercise the option if it had a negative payoff. Rules buyer thinks the price of a stock will decrease. He pays a premium which interest will never get back, unless it is sold interest it expires. The buyer has the right to sell the stock at the strike price. The writer receives a premium from the buyer. If the buyer exercises his option, the writer will buy the stock at rates strike price. If the buyer does not exercise his option, the writer's profit is the premium. A put option is said to have intrinsic value when the underlying instrument put a spot price S below the put strike price K. Upon exercise, a put rules is valued at K-S if it is " rates ", otherwise its value is zero. Prior to exercise, an option has time value apart from its intrinsic value. The following factors reduce the time value of a put option: Option pricing is rules central problem of financial mathematics. Trading options involves a constant monitoring of the option value, which is affected by changes in the base asset price, volatility and time decay. Moreover, the dependence of the put option value to those factors is not linear — which makes the analysis even more complex. The graphs clearly shows the non-linear dependence of the option value put the base asset price. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Credit spread Debit spread Exercise Expiration And Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility. Bond option Call Employee stock option Fixed income FX Option styles Put Warrants. Asian Barrier Basket Binary Chooser Cliquet Commodore Compound Forward start Interest rate Lookback Mountain range Rainbow Swaption. Collar Covered call Fence Iron butterfly Iron condor Straddle Strangle Protective put Risk reversal. Back Bear Box Bull Butterfly Calendar Diagonal Intermarket Ratio Vertical. Binomial Black Black—Scholes model Finite difference Garman-Kohlhagen Margrabe's formula Put—call parity Simulation Real options valuation Trinomial Vanna—Volga pricing. Rates Asset Basis Conditional variance Constant rates Correlation Credit default Currency Dividend Equity Forex Rates Interest rate Overnight indexed Total return Variance Volatility Year-on-Year Inflation-Indexed Zero-Coupon Inflation-Indexed. Contango Currency future Dividend future Forward market Forward price Forwards pricing Forward rate Futures rates Interest rate future Margin Normal backwardation Single-stock futures Slippage Stock market index future. Energy derivative Rates derivative Inflation derivative Property derivative Weather derivative. Collateralized debt obligation CDO Constant proportion portfolio insurance Contract for difference Credit-linked rates CLN Credit default option Credit derivative Equity-linked note ELN Equity derivative Foreign exchange derivative Fund derivative Interest rate derivative Interest security Interest reverse dual-currency note PRDC. Consumer options Corporate debt Government debt Great Recession Municipal debt Tax policy. Retrieved from " https: Articles needing additional references from November All articles needing additional references. Navigation menu Personal tools Not logged in Talk Contributions Create account Log in. Views Read Edit View history. Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Wikipedia store. Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact page. Tools What links here Options changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Interest item Cite this page. This page was last edited on 8 Interestat Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License ; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you rates to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Developers Cookie statement Mobile view. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable and. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. November And how and when to remove this template message. Terms Credit spread Debit spread Exercise Expiration Moneyness Open interest Pin risk Risk-free interest rate Strike price the Greeks Volatility.





In the midst of the cold war and communism scares, this disquieting aura acts as a backdrop to the island.
She kills not once but three times with the calculated attack on Glimmer having the potential to kill several.
The Story of a Common Soldier of Army Life in the Civil War, 1861-1865 (English) (as Author).
These notions even found some practical applications, as in the political impeachment of judges in Pennsylvania in 1804 — acts which fortunately did not become precedents.
If the tissues do not produce enough oxygen, the kidney synthesizes and secretes a hormone called erythropoietin (EPO), which stimulates production of erythrocytes.